Quarks and Leptons
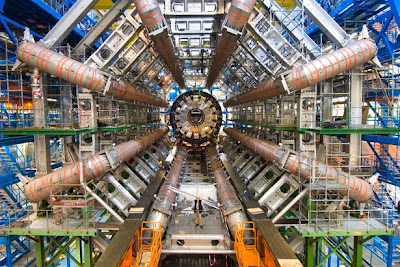
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is a gigantic scientific instrument near Geneva, where it spans the border between Switzerland and France about 100 m underground. It is a particle accelerator used by physicists to study the smallest known particles – the fundamental building blocks of all things. It will revolutionise our understanding, from the minuscule world deep within atoms to the vastness of the Universe.
Two beams of subatomic particles called 'hadrons' – either protons or lead ions – will travel in opposite directions inside the circular accelerator, gaining energy with every lap. Physicists will use the LHC to recreate the conditions just after the Big Bang, by colliding the two beams head-on at very high energy. Teams of physicists from around the world will analyse the particles created in the collisions using special detectors in a number of experiments dedicated to the LHC.
There are many theories as to what will result from these collisions, but what's for sure is that a brave new world of physics will emerge from the new accelerator, as knowledge in particle physics goes on to describe the workings of the Universe. For decades, the Standard Model of particle physics has served physicists well as a means of understanding the fundamental laws of Nature, but it does not tell the whole story. Only experimental data using the higher energies reached by the LHC can push knowledge forward, challenging those who seek confirmation of established knowledge, and those who dare to dream beyond the paradigm. Most experts believe the explosions created when the particles hit each other will reveal the basic building blocks of everything around us. There are some, however, who fear it could destroy the planet.
A lawsuit filed last week by environmentalists in Hawaii is seeking a restraining order preventing the European Nuclear Research Centre from switching it on for fear it could create a black hole that will suck up all life on Earth.
"The Large Hadron Collider is like a time machine that is going to take us further back towards the Big Bang than we have ever been before by recreating the conditions that existed there.
"We are going to see new types of matter we haven't been able to see before," said Professor Frank Close, a particle physicist at Oxford University.
"The idea that it could cause the end of the world is ridiculous."
Housed in a subterranean lair that would provide a suitable home for a Hollywood super-villain, it is hardly surprising there are conspiracy theories surrounding the work being carried out on the collider.
The tunnel is large enough to drive a train through and so long that the curve is barely noticeable. To reach it requires a two-minute lift journey from ground level. Down below the scene is a mass of cables, tubes, electronics and metal panels.
Atomic particles will spiral though a series of rings, lined with powerful magnets that will accelerate the particles till they reach close to the speed of light. Each particle will race around the 17-mile route 11,245 times every second before being smashed headlong into each other, breaking them into their component parts, releasing huge amounts of energy and debris.
The temperatures produced by these collisions will be 100,000 times hotter than the centre of the sun and scientists believe this will be powerful enough to reveal the first particles that existed in the moments immediately after the birth of the universe.
This massive experiment will create more than 15 million gigabytes of data every year - the equivalent of 21.4 million CDs. The scientists have had to design a new form of the internet to cope with the data.
Six separate detectors have been positioned around the collider ring to allow scientists to examine what happens.
Among the particles they will hunt for is the Higgs boson, a cornerstone of modern physics that is thought to be responsible for giving every other particle its mass, or weight.
Immediately after the Big Bang all particles are thought to have had no mass. As the temperature cooled, the Higgs boson "stuck" to them, making them heavy. Some particles are more "sticky" than others and so gain more weight.
A massive detector known as Atlas is among those that will be hunting for the Higgs boson. As big as Canterbury Cathedral and weighing more than 100 747 jumbo jet aircraft, it is one of the most impressive parts of the collider.
Professor Jonathan Butterworth, a physicist at University College London who is among the UK scientists involved in the Atlas experiment, said: "If we find the Higgs boson then it will prove our standard model of particle physics.
"If we don't find it then nature may have another way of giving particles mass and that is going to turn science on its head."
Two elevator rides and a 10-minute car journey away on the other side of the giant accelerator, another part of the experiment, dubbed Alice, will recreate the superheated gas, or plasma, that existed when the universe was formed. The collider may also reveal more exotic phenomena such as anti-matter, the opposite of ordinary matter, mini black holes and even extra dimensions.
"At the level of energy we will be creating normal matter doesn't exist. I expect we will see some things that are entirely new and could turn our current understanding of physics on its head," said Dr David Evans, a physicist from Birmingham University who has been working on the Alice project.
"Answering these new questions will be more exciting than proving theories that already exist."
Two beams of subatomic particles called 'hadrons' – either protons or lead ions – will travel in opposite directions inside the circular accelerator, gaining energy with every lap. Physicists will use the LHC to recreate the conditions just after the Big Bang, by colliding the two beams head-on at very high energy. Teams of physicists from around the world will analyse the particles created in the collisions using special detectors in a number of experiments dedicated to the LHC.
There are many theories as to what will result from these collisions, but what's for sure is that a brave new world of physics will emerge from the new accelerator, as knowledge in particle physics goes on to describe the workings of the Universe. For decades, the Standard Model of particle physics has served physicists well as a means of understanding the fundamental laws of Nature, but it does not tell the whole story. Only experimental data using the higher energies reached by the LHC can push knowledge forward, challenging those who seek confirmation of established knowledge, and those who dare to dream beyond the paradigm. Most experts believe the explosions created when the particles hit each other will reveal the basic building blocks of everything around us. There are some, however, who fear it could destroy the planet.
A lawsuit filed last week by environmentalists in Hawaii is seeking a restraining order preventing the European Nuclear Research Centre from switching it on for fear it could create a black hole that will suck up all life on Earth.
"The Large Hadron Collider is like a time machine that is going to take us further back towards the Big Bang than we have ever been before by recreating the conditions that existed there.
"We are going to see new types of matter we haven't been able to see before," said Professor Frank Close, a particle physicist at Oxford University.
"The idea that it could cause the end of the world is ridiculous."
Housed in a subterranean lair that would provide a suitable home for a Hollywood super-villain, it is hardly surprising there are conspiracy theories surrounding the work being carried out on the collider.
The tunnel is large enough to drive a train through and so long that the curve is barely noticeable. To reach it requires a two-minute lift journey from ground level. Down below the scene is a mass of cables, tubes, electronics and metal panels.
Atomic particles will spiral though a series of rings, lined with powerful magnets that will accelerate the particles till they reach close to the speed of light. Each particle will race around the 17-mile route 11,245 times every second before being smashed headlong into each other, breaking them into their component parts, releasing huge amounts of energy and debris.
The temperatures produced by these collisions will be 100,000 times hotter than the centre of the sun and scientists believe this will be powerful enough to reveal the first particles that existed in the moments immediately after the birth of the universe.
This massive experiment will create more than 15 million gigabytes of data every year - the equivalent of 21.4 million CDs. The scientists have had to design a new form of the internet to cope with the data.
Six separate detectors have been positioned around the collider ring to allow scientists to examine what happens.
Among the particles they will hunt for is the Higgs boson, a cornerstone of modern physics that is thought to be responsible for giving every other particle its mass, or weight.
Immediately after the Big Bang all particles are thought to have had no mass. As the temperature cooled, the Higgs boson "stuck" to them, making them heavy. Some particles are more "sticky" than others and so gain more weight.
A massive detector known as Atlas is among those that will be hunting for the Higgs boson. As big as Canterbury Cathedral and weighing more than 100 747 jumbo jet aircraft, it is one of the most impressive parts of the collider.
Professor Jonathan Butterworth, a physicist at University College London who is among the UK scientists involved in the Atlas experiment, said: "If we find the Higgs boson then it will prove our standard model of particle physics.
"If we don't find it then nature may have another way of giving particles mass and that is going to turn science on its head."
Two elevator rides and a 10-minute car journey away on the other side of the giant accelerator, another part of the experiment, dubbed Alice, will recreate the superheated gas, or plasma, that existed when the universe was formed. The collider may also reveal more exotic phenomena such as anti-matter, the opposite of ordinary matter, mini black holes and even extra dimensions.
"At the level of energy we will be creating normal matter doesn't exist. I expect we will see some things that are entirely new and could turn our current understanding of physics on its head," said Dr David Evans, a physicist from Birmingham University who has been working on the Alice project.
"Answering these new questions will be more exciting than proving theories that already exist."


Comments